Managing inactive mailboxes in Exchange Online is often complicated by overlapping retention policies, litigation holds, and compliance requirements. Sometimes, admins need to remove holds that are no longer necessary, but the process has traditionally been far more complex than it should be. They had to juggle multiple steps and clear holds one mailbox at a time.
But with Microsoft’s latest update, Exchange Online supports removal of holds from inactive mailboxes in a single operation using PowerShell. This new cmdlet is now available in Public Cloud. Let’s dive in!
Why Removing Holds from Inactive Mailboxes Matters?
Inactive mailboxes often stay locked by retention policies or labels, due to compliance reasons. Admins may still find the need to remove holds from inactive mailboxes for the following reasons:
- Free up storage by clearing unnecessary or outdated data.
- Simplify compliance management by removing obsolete retention settings.
- Enable faster offboarding of users without manual intervention.
- Support automation and bulk cleanup across multiple inactive mailboxes.
New ExcludeFromAllHolds Parameter to Remove Retention Holds from Inactive Mailboxes
The new ExcludeFromAllHolds is an opt-in parameter introduced by Microsoft to help admins efficiently removes all applicable holds except eDiscovery holds, litigation hold, and restrictive retention policies. Once the holds are removed, the mailbox transitions to a soft-deleted state, and it will be permanently deleted after 30 days.
For example, A company is reorganizing and wants to permanently delete 500 old inactive mailboxes. Instead of manually removing dozens of different holds per mailbox, an admin can now run a single PowerShell command per mailbox (or in bulk) to remove all non-critical holds and safely delete them.
Sometimes, admins don’t need to remove all holds. They may want to adjust only Compliance Tag enforcement on a mailbox. The RemoveComplianceTagHold switch is designed for this scenario.
Let’s see the core differences between these parameters:
| ExcludeFromAllHolds | RemoveComplianceTagHold |
| Removes all applicable holds from an inactive mailbox in a single action, including: 1. Organization-level retention policies 2. User-level retention policies 3. Delay Holds 4. Compliance Tag holds | Removes only the Compliance Tag–based hold from the mailbox, leaving all other holds intact. |
| Preserves critical holds such as: 1. In-Place eDiscovery holds 2. eDiscovery case holds 3. Litigation holds 4. Restrictive retention policies | All other holds remain unaffected, including: 1. eDiscovery 2. Litigation 3. Restrictive retention policies 4. Organization/user-level retention policies |
| Ideal for bulk cleanup, mailbox decommissioning, or lifecycle management when you need to remove multiple types of holds efficiently while maintaining compliance. | Provides granular control to clear Compliance Tag–based holds, allowing retention label logic to be updated without impacting other holds. |
Note: Holds removed using ExcludeFromAllHolds or RemoveComplianceTagHold cannot be undone. After removal, the Email Lifecycle Assistant may automatically reapply Compliance Tag holds on items that are still labeled. To ensure proper compliance, admins must manually apply any new retention policies to these items.
How to Remove Holds from Inactive Exchange Objects Using PowerShell?
You can remove holds from a single inactive exchange objects or process them in bulk using PowerShell. But, before running the commands, make sure the following pre-requisites are met.
Pre-requisites for Removing Inactive Mailbox Holds
- Connect to Exchange Online PowerShell.
- Ensure the mailbox is inactive (soft-deleted).
- Have the required RBAC roles assigned, including Mailbox Import Export, Retention Management, and eDiscovery Manager.
- Review existing holds and confirm that legal or regulatory obligations are met.
You can remove the holds for the below Exchange Online objects:
1. Remove Holds from Inactive User Mailboxes
You can remove holds from inactive user mailboxes either completely with ExcludeFromAllHolds or selectively with RemoveComplianceTagHold. Let’s see how.
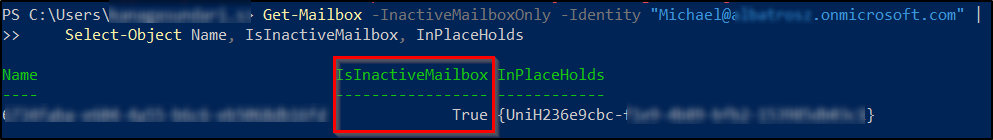
Verify Inactive Mailbox Status
Before removing any holds, first confirm that the mailbox is truly inactive and still has preservation holds attached. Replace the placeholder <user@contoso.com> to specify the inactive mailbox you want to check.
|
1 2 |
Get-Mailbox -InactiveMailboxOnly -Identity "<user@contoso.com>" | Select-Object Name, IsInactiveMailbox, InPlaceHolds |
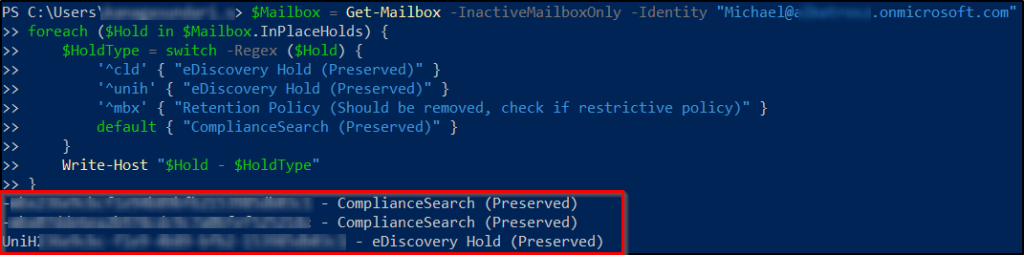
Identify Hold Types Applied to an Inactive Mailbox
If you want to remove selective or specific holds on an inactive mailbox, use the PowerShell cmdlet below to first review and classify all existing holds. This helps you identify which holds must be preserved and which ones are safe to remove. Replace <user@contoso.com> before running the script.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
$Mailbox = Get-Mailbox -InactiveMailboxOnly -Identity "<user@contoso.com>" foreach ($Hold in $Mailbox.InPlaceHolds) { $HoldType = switch -Regex ($Hold) { '^cld' { "eDiscovery Hold (Preserved)" } '^unih' { "eDiscovery Hold (Preserved)" } '^mbx' { "Retention Policy (Should be removed, check if restrictive policy)" } default { "ComplianceSearch (Preserved)" } } Write-Host "$Hold - $HoldType" } |
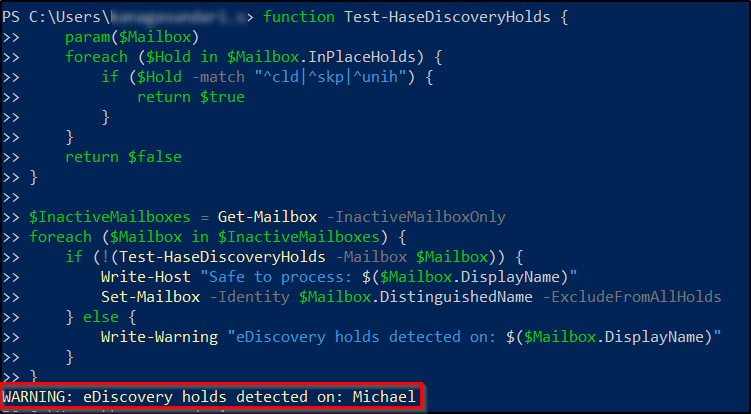
Identify Inactive Mailboxes With eDiscovery Holds
Before bulk-removing holds, use this pre-validation script to identify inactive mailboxes with eDiscovery holds, ensuring you only process those that are legally safe to modify.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
function Test-HaseDiscoveryHolds { param($Mailbox) foreach ($Hold in $Mailbox.InPlaceHolds) { if ($Hold -match "^cld|^skp|^unih") { return $true } } return $false } $InactiveMailboxes = Get-Mailbox -InactiveMailboxOnly foreach ($Mailbox in $InactiveMailboxes) { if (!(Test-HaseDiscoveryHolds -Mailbox $Mailbox)) { Write-Host "Safe to process: $($Mailbox.DisplayName)" Set-Mailbox -Identity $Mailbox.DistinguishedName -ExcludeFromAllHolds } else { Write-Warning "eDiscovery holds detected on: $($Mailbox.DisplayName)" } } |
Remove All Holds from a Single Inactive Mailbox
Now, you can remove all retention and in-place holds from a specific inactive mailbox using the following PowerShell cmdlet. Replace the <user@contoso.com> placeholder before running the cmdlet.
|
1 |
Set-Mailbox -Identity "<user@contoso.com>" -ExcludeFromAllHolds |

Remove Specific Holds Using RemoveComplianceTag
To remove just the Compliance Tag–based hold from an inactive mailbox without affecting other retention or in-place holds, run the below cmdlet by replacing the <user@contoso.com> placeholder.
|
1 |
Set-Mailbox -Identity “<user@contoso.com>" -RemoveComplianceTagHold |
To verify compliance tag removal: After removing the compliance tag hold, to check that it has been cleared while other holds remain intact, run the Get-Mailbox cmdlet by replacing <user@contoso.com>
|
1 |
Get-Mailbox -InactiveMailboxOnly -Identity “<user@contoso.com>" | Select-ObjectName, InPlaceHolds, ComplianceTagHoldApplied, DelayHoldApplied, DelayReleaseHoldApplied |
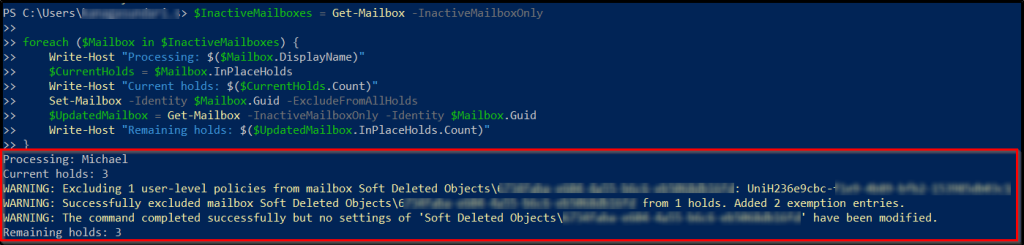
Bulk Removal of Holds from Multiple Inactive Mailboxes
If you need to process bulk execution, you can remove all the retention holds from multiple inactive mailboxes by using the Set-Mailbox cmdlet.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
$InactiveMailboxes = Get-Mailbox -InactiveMailboxOnly foreach ($Mailbox in $InactiveMailboxes) { Write-Host "Processing: $($Mailbox.DisplayName)" $CurrentHolds = $Mailbox.InPlaceHolds Write-Host "Current holds: $($CurrentHolds.Count)" Set-Mailbox -Identity $Mailbox.Guid -ExcludeFromAllHolds $UpdatedMailbox = Get-Mailbox -InactiveMailboxOnly -Identity $Mailbox.Guid Write-Host "Remaining holds: $($UpdatedMailbox.InPlaceHolds.Count)" } |
2. Remove Holds from Inactive Mail Users
If a former employee’s mailbox was converted to a mail user for directory reference, but is no longer needed for legal or business purposes, it may remain locked by retention or compliance holds. Using –ExcludeFromAllHolds, you can clear all such holds from the inactive mail user, allowing the mailbox to be fully cleaned up or permanently deleted after verification of its remaining hold status.
Get the Inactive Mail User
Retrieve the inactive (soft-deleted) mail user to perform hold removal operations by replacing “<user@contoso.com>” and running the cmdlet below.
|
1 |
$MailUser = Get-MailUser -Identity "<user@contoso.com>" -SoftDeletedMailUser |
Exclude the Inactive Mail User from All Holds
Remove the mail user from all applicable retention and compliance holds using the ExcludeFromAllHolds switch.
|
1 |
Set-MailUser -Identity $MailUser.ExchangeGuid -ExcludeFromAllHolds |
Verify the Inactive Mailbox State and Holds
Check the mailbox state and remaining holds to ensure that the exclusion was successful using Get-MailUser.
|
1 |
Get-MailUser -SoftDeletedMailUser -Identity $MailUser.ExchangeGuid | Select-Object Name, IsInactiveMailbox, InPlaceHolds |
3. Remove Holds from Inactive Group Mailbox
If your organization no longer uses a Microsoft 365 Group that has completed its work, the group mailbox often remains locked by retention or compliance holds, blocking mailbox clean up or full deletion. With new PowerShell parameters, you can now remove those holds from an inactive group mailbox in one go, making it easier to retire old project groups while still confirming any holds that need to stay in place.
Get the Inactive Group Mailbox
Retrieve the inactive group mailbox by replacing <user@contoso.com> in the below cmdlet to prepare for hold removal.
|
1 |
$Group = Get-Mailbox -Identity "<user@contoso.com>" -SoftDeletedMailbox -GroupMailbox |
Exclude the Inactive Group Mailbox from All Holds
Remove the group mailbox from all applicable retention and compliance holds using ExcludeFromAllHolds as shown below.
|
1 |
Set-Mailbox -Identity $MailUser.ExchangeGuid -ExcludeFromAllHolds -GroupMailbox |
Verify the Inactive Group Mailbox State and Holds
Check the mailbox state and remaining holds by running the below cmdlet to ensure that the exclusion was applied successfully.
|
1 |
Get-Mailbox -Identity "<user@contoso.com>" -SoftDeletedMailbox -GroupMailbox | Select-Object Name, IsInactiveMailbox, InPlaceHolds |
That’s it, I hope this blog helped you understand how to remove holds from inactive exchange objects and streamline your Microsoft 365 clean-up process. If you have any questions, feel free to reach out in the comments below!