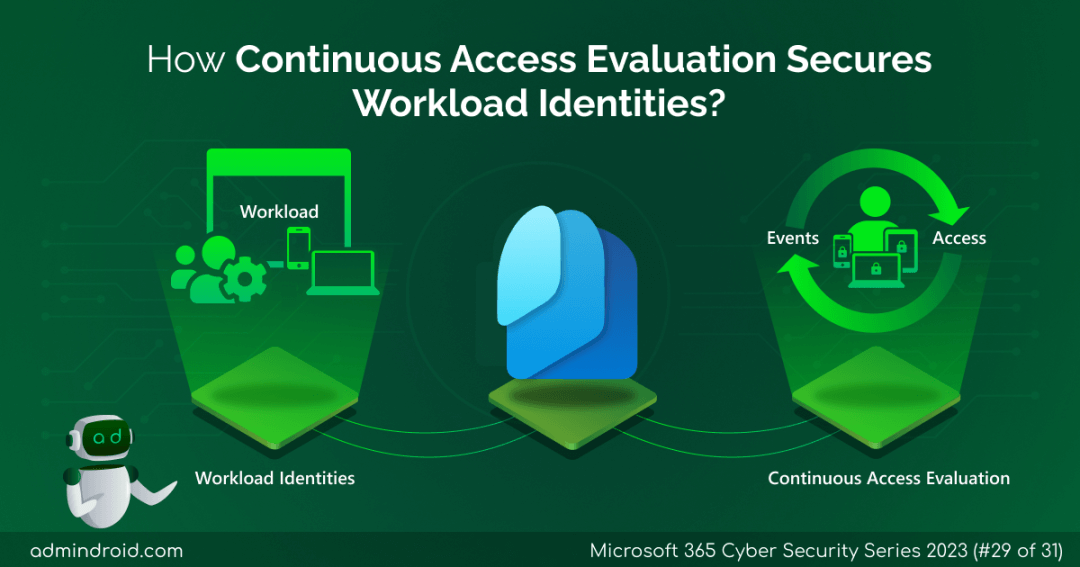
On Day 29 of Cybersecurity awareness month, let’s dive into how Continuous Access Evaluation for workload identities protection works within Microsoft Entra ID. Stay tuned for our more blogs in the M365 Cybersecurity blog series.
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern digital infrastructure, workload identities play a pivotal role in representing your applications within the Microsoft Entra ID. They allow you to securely authenticate and access other resources, such as Microsoft Graph, Entra storage, or your own APIs, without exposing user credentials. However, workload identities also come with some security challenges, such as:
- They don’t have a structured lifecycle management process.
- They lack the ability to utilize multifactor authentication (MFA).
- They require storage space to store credentials.
These challenges increase the risk of workload identities from being compromised. There is one solution that will help you solve these challenges: Continuous Access Evaluation for workload identities. Let’s get started!
In an age where information is a valuable commodity, security is paramount.
– Robbie Sinclair
What is Continuous Access Evaluation for Workload Identities?
Continuous Access Evaluation (CAE) in Azure AD is a mechanism that enables real-time enforcement of Conditional Access policies and risk policies, as well as token revocation events for workload identities. In Microsoft Entra, workload identities refer to applications, service principals, and managed identities.
When workload identities seek access to resources like the Microsoft Graph API, Microsoft Entra ID issues them access tokens. These tokens typically remain valid for a specific period, and during this time, Microsoft Entra ID doesn’t actively assess authorization conditions. Even when an admin revokes access, the identity can still have access until the token expires.
However, with CAE enabled, Microsoft Entra ID can proactively inform resource providers about changes in conditions that could impact the tokens’ validity in near-real time. As a result, resource providers have the capability to prompt workload identities to reauthenticate, securing new tokens when necessary.
What does Continuous Access Evaluation for Workload Identities Support?
It’s important to note that CAE for workload identities has a specific scope of support. The following are supported by continuous access evaluation for workload identities.
- Currently, workload identities are supported on access requests sent to Microsoft Graph. However, Microsoft plans to expand this support to more resource providers in the future, making it an even more versatile security solution.
- Service principals for line of business (LOB) applications are supported, ensuring that a wide range of applications can benefit from CAE.
- CAE for workload identities supports various revocation events, including:
- Service Principal/Application Disable: When a service principal/application is disabled, CAE ensures that the access is immediately revoked.
- Service Principal/Application Delete: Similarly, if a service principal/application gets deleted, CAE takes swift action to revoke access.
- High Service Principal Risk: CAE analyzes Microsoft Entra ID protection to detect high service principal risk and revoke access accordingly.
- In addition to this, Conditional Access policies that target both location/IP range as well as risk policies are supported.
What is the License Requirement for Continuous Access Evaluation?
By default, Continuous Access Evaluation is enabled for all Microsoft Entra ID tenants. To customize CAE settings, you will need a Microsoft Entra ID Premium (P1 or P2) license, as CAE is configured through conditional access policies.
How CAE Secure Workload Identities?
Continuous Access Evaluation (CAE) is indeed a significant security upgrade for the Microsoft 365 environment, and it extends to various workload identities. Find the real-time use cases on how CAE works in apps, service principles, VMs, and more.
Real-time Use Cases:
- App running on a VM: Suppose you have an app running on a VM that uses a service principal to access a database. If the service principal is disabled or deleted, CAE can inform the database almost immediately. The database can then prompt the app to reauthenticate, securing a new token when necessary.
- Service Principle: Consider a service principle used by an automated system to access various resources. If the service principle is compromised and flagged as high risk by Microsoft Identity Protection, CAE can inform the resource providers in near-real time. The resource providers can then prompt the automated system to be reauthenticated.
- Password Compromise Response: In the event of a password compromise on an application, administrators can use CAE to instantly revoke all active sessions and reset passwords.
For example, let’s say an application running on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) has its password compromised. With CAE, administrators can instantly revoke all active sessions and reset passwords. This immediate action prevents unauthorized access and secures the application’s workload identity.
- Insider Threat Protection: CAE safeguards against malicious insiders trying to misuse access tokens and rejecting access attempts from unauthorized IP addresses.
For example, suppose a malicious threat actor steals the access token and tries to misuse them, CAE safeguards by enforcing CA location and risk policies. Also, if any access requests come from an unauthorized IP address, CAE will reject it.
- Location-Based Access Control: CAE will provide access control based on authorized locations to avoid unauthorized access to workload identities.
For example, Imagine a user has access to an application only from a specified location. If the user tries to access the application from unapproved location, CAE will the block the access, thereby preventing exposure of sensitive information.
As seen above, CAE is particularly useful for managing workload identities such as apps. Let’s dive into how to manage CAE for applications to secure the data.
Manage Continuous Access Evaluation for Applications
Learn how to enable, disable, and verify CAE for applications.
- Enable Continuous Access Evaluation for applications
- Disable Continuous Access Evaluation for applications
- Verify Continuous Access Evaluation activity
How to Enable Your Application for Continuous Access Evaluation?
To enable your application for Continuous access evaluation, you need to request xms_cc as an optional claim in your token requests.
To request xms_cc as an optional claim, you can follow these steps:
- Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as an application administrator.
- Navigate to Applications > App registrations.
- Select one of the applications based on requirements.
- Under ‘Manage’, select Token Configuration.
- Select Add optional claim and choose Access for the token type.
- In the Optional claims pane, select Add new claim and enter xms_cc in the name field.
- Select Add.
Note – You can also use JSON code to request xms_cc as an optional claim.
|
1 |
Claims: {"access_token":{"xms_cc":{"values":["cp1"]}}} |
The xms_cc claim with a value of cp1 in the access token is the authoritative way to identify that a client application is capable of handling claim challenges. This feature provides developers with the ability to enhance the security of their applications.
How to Disable Continuous Access Evaluation?
If, for any reason, you wish to opt out of CAE, simply refrain from sending the xms_cc claim with a value of cp1. It’s important to note that organizations with Microsoft Entra ID P1 or P2 subscriptions can create Conditional Access policies to disable continuous access evaluation applied to specific workload identities as an immediate stop-gap measure.
How to Verify CAE Activity?
In some cases, CAE may block a client’s access to a resource, triggering a need for reauthentication. This behavior is essential for maintaining security. To troubleshoot and verify CAE activity, follow these steps:
- Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as a Conditional Access Administrator.
- Navigate to Identity > Monitoring & Health > Sign-in Logs > Service Principal Sign-ins.
- Use filters to streamline the debugging process.
- Select an entry to view activity details and look for the “Continuous access evaluation” field to determine whether a CAE token was issued in a particular sign-in attempt.
Final Thoughts
Continuous Access Evaluation for workload identities is a valuable security tool that can significantly enhance your organization’s security posture. Just as CAE enhances security for workload identities, Microsoft also support for CAE in Microsoft 365 admin center. This ensures that access policies are enforced in near real-time for admin center sessions, eliminating the delay associated with token expiration.
I hope this blog guided you through the concepts of Microsoft Entra ID Continuous Access Evaluation role in workload identity protection. Feel free to reach us in the comments for any assistance.