On Day 17 of Cybersecurity awareness month, learn to deploy least privilege access across your organization and reduce insider risks. Stay tuned for more blogs in the Cybersecurity blog series.

Does your organization grant multiple access rights to users? Then you are in grave danger! Because users in some organizations have access and permissions beyond what would be required to perform their daily tasks.
- Researchers estimate that improper access control leads to the loss of millions of dollars each year.
- Forrester’s research estimates that at least 80% of security breaches involve privileged credentials.
- Also, once Microsoft worried that “most security-related training courses and documentations discuss the implementation of a principle of least privilege, yet organizations rarely follow it.“
That’s a lot of analysis, isn’t it? If excessive privileges pose such a massive threat, why don’t organizations pull it out entirely? But there is no serious concern about how access control is handled in Office 365.
So with the rate of cyber threats on the rise, organizations must change their cybersecurity strategies and implement security measures such as least privilege access, unmanaged device restrictions, etc. Having less access privilege reduces security risks and business disruptions. Moreover, the zero-trust strategy relies heavily on least privilege access to achieve its objectives.
The Best Defense for Insider Risks- Least Privilege Access:
What is least privilege access?
Users, admin accounts, and computing processes should be restricted to access only those resources required to perform their tasks. Therefore, users are granted only the necessary authority for specific activities, tasks, or resources.
The purpose of least privilege access is to prevent users, administrators, applications, or different services from having “overprivileged access.” By doing so, organizations can ensure that the right people have access to the right resources under the right circumstances.
Gain the Entire Benefits of Least Privileged Access:
Therefore, least privileged access allows users to perform privileged tasks under trusted policy guidelines and reduce security risks. Following are some of the benefits,
- Too many over-privileged users are always a risk – IAM reports that three-quarters of organizations are assigning more privileges than are needed to their users. Therefore, users must have least-privileged or required-privilege access.
- Reduce malware incidents – When the principle of least privileged access is applied at the endpoints, malware cannot migrate into highly privileged accounts.
- Seamless user experience – Granting access only to what users require and locking down unnecessary user privileges reduces the burden on employees and increase user productivity & efficiency.
- Attain regulatory compliance – Organizations are now mandated to implement the least privilege regime as part of their security practices. In this way, systems are protected from malicious or erratic damage.
When to Implement Least Privilege Access?
In the following section, we will discuss when the great defense mechanism should be implemented.
Cyber attackers often target privileged accounts because gaining access to a highly privileged account can help them access everything. Finally, one compromised user with local administrator privilege is enough to take complete control and steal the most sensitive data. So, Microsoft suggested a descriptive idea of when to implement the least privileged access.
For example, if an administrator logs on with a privileged account and inadvertently runs a virus program, the virus has administrative access to the local computer and the entire domain. If the administrator had instead logged on with a non-privileged (non-administrative) account, the virus’s scope of damage would only be the local computer because it runs as a local computer user, Microsoft said.
Thus, least privileged access should be your organization’s first line of defense against data breaches.
Guidelines to Deploy the Least Privilege Access Strategy
Having recognized the importance of least privileged access, now it’s time to set it up in your Office 365 tenant. So, we’ve outlined a set of guidelines you must follow to deploy the least privileged access below.
Step 1: ‘Identify’ all the existing highly privileged accounts. Get a complete view of all the local administrator and domain administrator accounts, as they hold many sensitive data.
Step 2: ‘Validate’ the existing privileges, such as who has access to which applications, systems, servers, devices, etc.
Step 3: ‘Revoke’ all unnecessary & unused privileges and make sure no extra privileges are granted to any users.
Step 4: ‘Monitor’ all the accounts that are provisioned for high-privileged roles (administrator accounts).
Step 5: ‘Grant’ only just-in-time access and just enough access for the accounts whenever necessary.
Step 6: ‘Review’ – Review permissions granted to all applications, users, or other cloud-based environments. Implement privileged access management in your organization to work with zero-standing privileges and have a deeper level of security against suspicious vulnerabilities.
Incorporating all these steps into your security plan will significantly reduce the risks due to high-privileged accounts. In today’s threatening landscape, where risks and breach rates are constantly rising, least-privilege access is more than just a smart idea. By doing so, an organization can improve its security standards and empower its cyber-fatigue environment.
What is Privileged Access Management in Office 365?
Too many over-privileged users can be a serious security threat to your organization. So, to overcome all the hardships, Microsoft introduced privileged access management in Office 365.
Privileged access management means granular control over your privileged tasks in Office 365. With PAM, you can grant control to users based on a just-in-time and just-enough-access approach. The administrator or user will only be granted access when it is necessary. After the task completion, it revokes the granted permissions for the admin/users.
Thus, you can protect critical assets in your organization and comply with compliance regulations. Generally, PAM is available in Azure AD Premium P2 license. Also, it is necessary to have a P2 license for users who submit or respond to requests for privileged access management.
Workflow of PAM:
Privilege access management prevents users from having privileges assigned to them for a long time. It works in a time-bounded system.
Users must request privileges if needed, and the approvers decide whether to grant or deny access. Once permission is granted, users can perform the privileged task within the time duration (default 4 hours). But users cannot access the tasks after the time limit has expired. Thus, it helps in preventing insiders from causing threats.
Step-by-Step Instruction to Setup PAM: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/compliance/privileged-access-management-configuration
RBAC – The Dynamic Approach to Basic Licensing Packages:
As we already know, Office 365 PAM requires an Azure AD Premium P2 license. So, what about organizations that don’t hold it? No worries! Implement a role-based access control (RBAC) approach to delegate different roles to users in your organization. The good news is that RBAC is part of the free subscriptions!
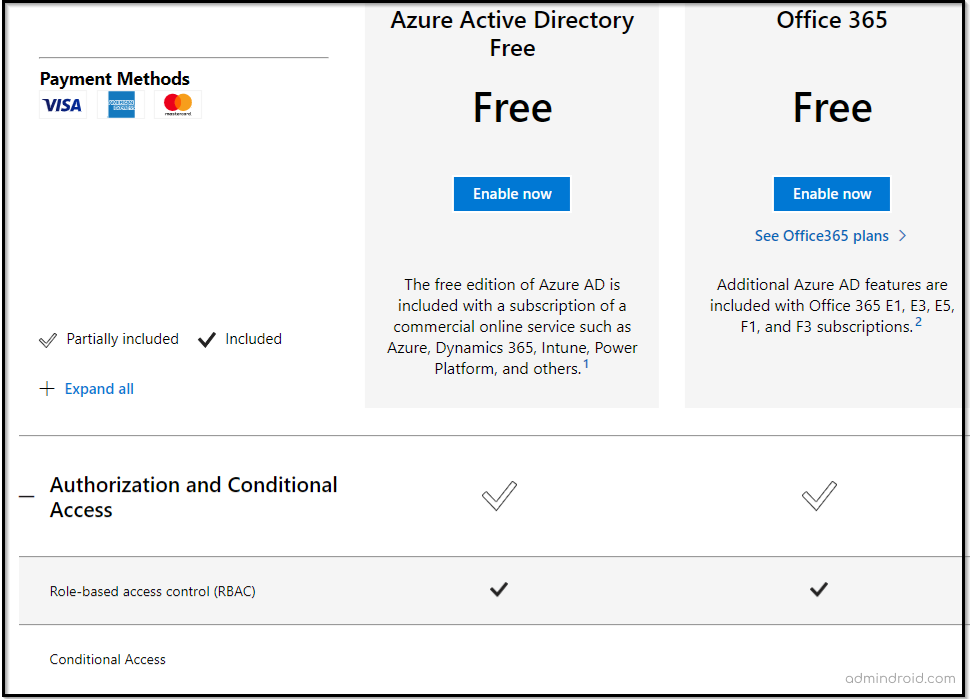
What is Role-based access control in Office 365?
Role-based access control restricts user access based on assigned roles within an enterprise. Using RBAC and JIT access helps maintain strict governance and personal data protection, by ensuring that administrative rights are granted only when necessary and revoked promptly.
Based on the Role Based Access Control (RBAC) permissions model, Exchange Online and Office 365 come with numerous predefined permissions. You can assign admin roles and access permissions using Microsoft 365 admin center and Exchange Online.
Assign an Admin Role for Users Using Microsoft 365 Admin Center:
Microsoft 365 admin center has a huge list of admin roles that can be granted to your Office 365 users. You can assign admin roles like Global administrator, Teams administrator, Exchange administrator, Helpdesk administrator, etc., from the admin center. All the roles available in the admin center are tenant-wide granted roles. There is no particular granular delegation to specific tasks or activities in the admin center.
Steps to assign admin roles using Office 365 admin center: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/admin/add-users/assign-admin-roles
Role-based Access Control in Exchange Online:
As Exchange Online holds a majority of the Office 365 tasks in an organization, there is a detailed role-based access control approach is available. With Exchange Online, you can granularly delegate and assign permissions to different activities, settings, etc.
Detailed step-by-step procedure to setup role-based access control in Exchange Online: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/exchange/permissions-exo/permissions-exo
Using RBAC efficiently increases IT productivity, saves time, reduces costs, and tightens security. Even though RBAC is less granular than assigning access rights per user, it is more secure since it has less error-prone.
At the end of the day, the goals are simple: safety and security.
-Jodi Rell
Finally, I hope we have provided you with enough ideas and suggestions about granularly delegating access, permissions, and tasks on this topic. Ensure a cyber fatigue-free environment by implementing the appropriate steps. To further strengthen your security posture, use Microsoft Entra Private Access, which utilizes Zero Trust principles, including least privilege, to provide secure access to internal applications and resources.
If you need assistance with ideas on least privilege access, feel free to reach us on our platforms. We would be glad to provide suggestions for your queries!