On Day 11 of Cybersecurity awareness month, learn about leaked credential detection to combat account compromises. Stay tuned for the upcoming blogs in M365 Cybersecurity blog series.
When do you typically find out that your Microsoft 365 credentials have been compromised? Too often, it’s after the attacker has already broken into your system. But imagine if there was a way to detect leaked credentials before they could be used for malicious purposes. That would be a game-changer, right? 💯
Well, the good news is that Microsoft has made it possible! They offer leaked credential detection report in Microsoft Entra ID as part of Entra ID protection. Also, this risk detection supports detecting leaked credentials for workload identities. The leaked credentials are nothing but the credentials that have been stolen by the cyber attackers.
So, with Entra ID’s risk detection capability, you can proactively identify users whose credentials have been leaked. And with this, you can take swift action to prevent data breaches.
Wait, here is the best part – the ‘Leaked Credentials’ report is available to you absolutely free, while a few other reports may require Azure AD Premium P2 or other licenses.
Interesting? Then don’t delay! Explore this risk detection and identify credential leaks in your organization.
How does Microsoft Find Leaked Credentials?
First, let’s see how the credential leakage is done and then proceed to see how Microsoft identifies! In most cases, when attackers acquire credentials through phishing or ransomware attacks, approximately 70% of them tend to share this information across various platforms. This includes sharing it on public password dump sites, the dark web, public GitHub repositories, and paste sites such as pastebin.com and paste.ca. These websites are usually the first places bad actors go to post stolen credentials. In some cases, they may even engage in trading and selling those stolen details on the black market!
So, Microsoft employs its AI technologies to collect those leaked credentials and cross-reference them with the current credentials of Entra users. If there’s a match, they tag it as “leaked credential” and expose it on the risk detection page within Entra ID protection.
However, it’s crucial to note that Microsoft’s system will not notify you about leaked credentials if you have not enabled Password Hash Synchronization (PHS) in your organization.
- PHS involves storing password hashes in databases, which are cryptographic representations of passwords typically used for authentication purposes. The leaked credential service uses these password hashes for cross-checking with credentials found on the dark web.
- So, you should enable password hash synchronization with Microsoft Entra Connect.
Now that we have a good understanding of how Microsoft’s detection process is, let’s proceed to investigate the leaked credential report within Entra ID Protection.
Analyze Leaked User Credential Detection Report in Microsoft Entra ID
Microsoft’s machine learning and AI technology actively scan for credential pair matches with the current ones. When a match is detected, it promptly notifies admins through the “Risk detection” report. To view the report, you can follow the navigation below.
Microsoft Entra admin center → Protection → Identity Protection → Risk detections
Note: You should apply the filter “Detection type: Leaked Credentials” to specifically retrieve logs related to credential compromise events.
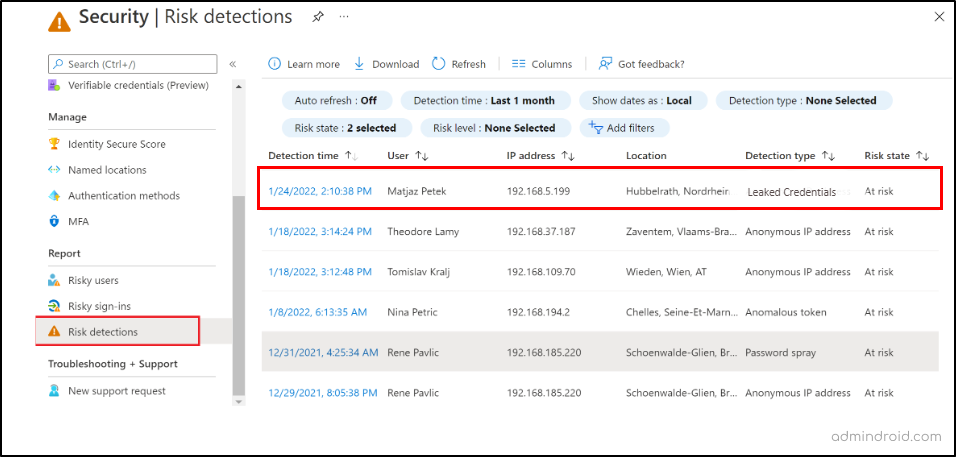
The leaked credential report as part of Entra ID Protection gives you clear information on which user’s credentials have been compromised, the associated risk state, risk levels (high, medium, low), and a lot more.
- Identify Compromised User Accounts: Pinpoint which specific user accounts have had their credentials compromised and take immediate action to secure these accounts.
- Risk Assessment: It provides a risk state for each compromised account. Understanding the severity of the risk helps you prioritize which accounts to address first.
- Incident Response: With this report, you can quickly initiate an incident response plan for affected users, including password resets, account lockouts, or further investigation.
Admins can also utilize the “Azure AD risky users report” to pinpoint users at risk, often associated with credential compromises and risky sign-in attempts. This report offers additional information about the detections, sign-in history, and the user’s risk history.
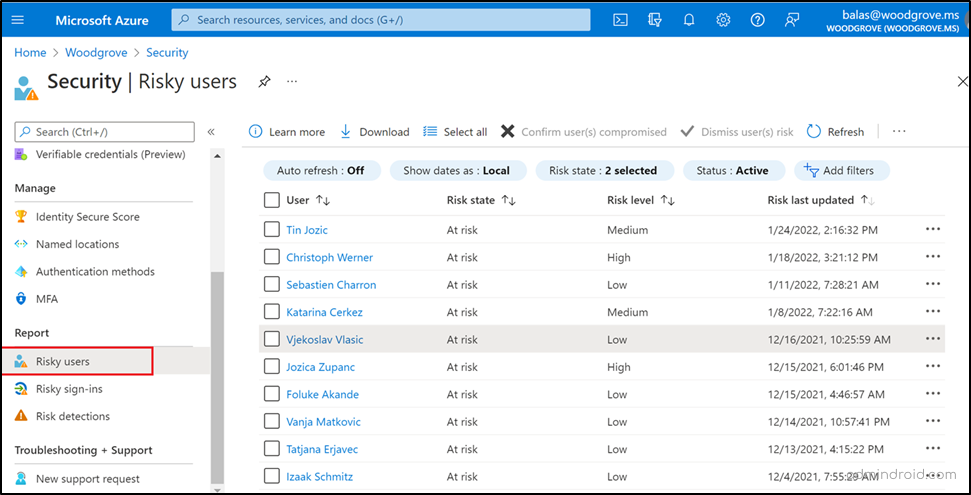
After a thorough review of these reports, admins can act by setting MFA, requiring password resets to enhance security measures in the organization.
Remedial Action: MFA and Password Reset for Credential Leaked Users
When a leaked credential detection pops up in your organization, don’t just nod and walk away! You should take proactive security measures to lock out attackers and strengthen your organization’s defenses. Here are two key security features to consider:
Block User Accounts with Leaked Credentials:
- You can temporarily block user accounts associated with compromised credentials to prevent potential attackers from gaining access to the organization.
Monitor the Activity of Users with Leaked Credentials:
- You need to monitor the victim users to detect any unusual or malicious actions taken by them threatening the organization.
Educate Users About the Importance of Strong Passwords:
- Admins need to educate users to set strong password for their account, which could prevent them from account compromises.
Update Security Policies and Procedures:
- You should update the security policies and procedures to strengthen the defense against leaked credentials.
Investigate the Source of the Credential Leak:
- Admins should compel their security teams to investigate the source of the data leak, allowing for preventive measures against future data breaches.
Here are the two major actions that need to be taken once you detect the credential leakages.
Force Users to Reset Passwords:
- For users with compromised credentials, it’s crucial to initiate a password reset immediately. This ensures that the attackers’ stolen credentials become ineffective for unauthorized access attempts.
Enable Multi-factor Authentication (MFA):
- Admins must ensure that MFA is activated for all users, and if it’s not, they should promptly enable it to enhance security.
Among the security measures, blocking affected accounts, requiring password resets, and enabling MFA are the crucial steps you need to take after detecting the leaked credentials.
To accomplish the objectives mentioned above, administrators can leverage two important security policies within Microsoft Entra ID:
- User risk policy in Microsoft Entra ID Protection
- Configure user-risk based Conditional Access policy
These policies are your frontline defense, automating actions on impacted users in Microsoft 365. They seamlessly trigger actions such as blocking sign-ins, timely password changes, and strengthening M365 security by requiring multifactor authentication. So, let’ see how to effectively configure these policies in your organization to defend against potential threats.
Note: It’s a smart move to configure it in advance before any potential risks rear their heads.
Create User Risk Policy in Microsoft Entra ID
A user risk policy within Entra ID Protection can be configured to prompt password resets automatically for users when detected for risks like leaked credentials, failed MFA attempts and some more.
- Entra ID Protection continuously monitors user activity for signs of risk. When a user is detected at risk, Entra ID Protection triggers the appropriate policy, such as requiring a password reset. The user is then prompted to create a new, strong password. Once the user has reset their password, they can regain access to their account!
- This eliminates the need to manually inform users about the necessity of a password reset when any user risk detection is identified.
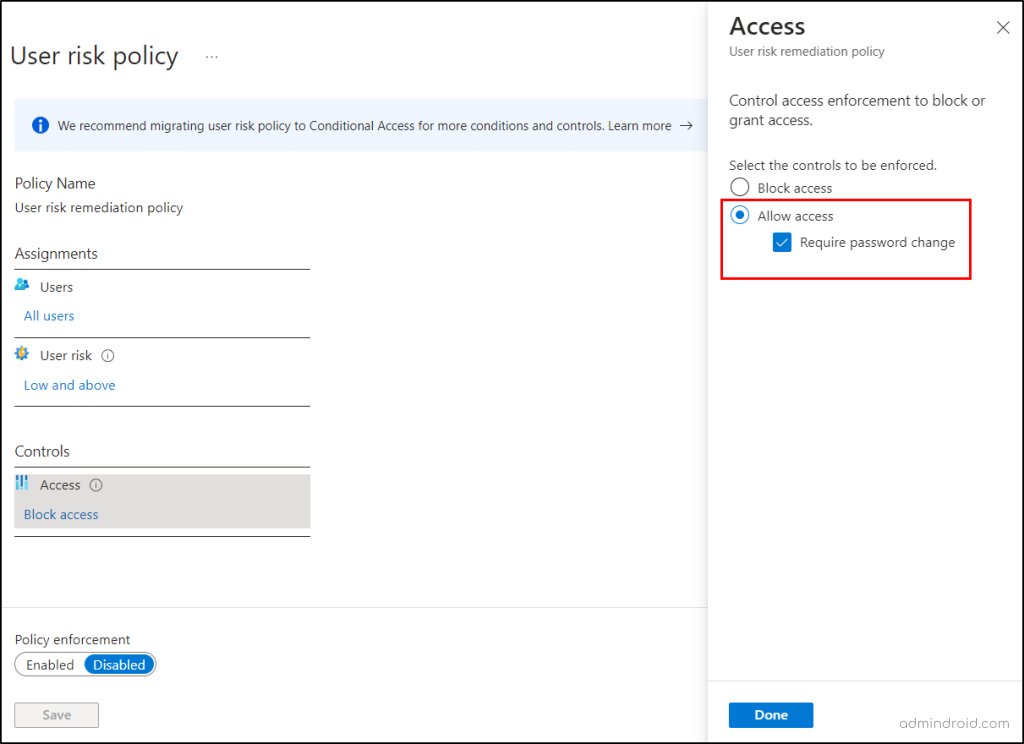
To configure the user risk remediation policy in Entra ID protection, follow the steps below.
- Navigate to Microsoft Entra admin center → Protection → Identity Protection → User risk policy.
- Assignments > Users> All Users.
- User risk> Low and above.
- Controls > Access > Allow Access > Require password change >Done.
Alternate solution: Select Block access, if you want to block the account.
- Finally, enable the policy and continue to save the policy.
Important Thing to Note:
It’s essential to keep in mind that enabling password resets alone can pose a security loophole. For instance, if an attacker obtains credentials from the dark web and attempts to use them, they may be triggered by a password reset prompt. This makes it a straightforward option for them to fully compromise Microsoft 365 security. To help prevent credential leaks, always use secure methods to store passwords and secrets used in automation scripts instead of embedding passwords directly in code.
To address this vulnerability, it’s advisable to implement a policy that requires both multi-factor authentication (MFA) and a password change when necessary. This approach adds an extra layer of security and ensures that users who genuinely require a password reset are protected. So, utilizing user-risk detections within Conditional Access policies to enforce MFA and password changes is a more robust and secure strategy. Let’s see that in detail below.
Configure User-risk Based Conditional Access Policy
User risk detection + Conditional Access = Two powerful security features to implement highly granular and effective access control measures.
- User risk detection – Identifies users who may be at risk due to factors such as compromised credentials, suspicious activity, or risky sign-in attempts.
- Conditional Access – Allows organizations to define rules that control how users access resources based on their risk level, device type, location, and other factors.
By combining user risk detection with Conditional Access, organizations can create more secure and adaptable access control policies. For example, an organization could create a policy that requires multi-factor authentication, password resets for all users who have a high user risk score, before accessing any resources.
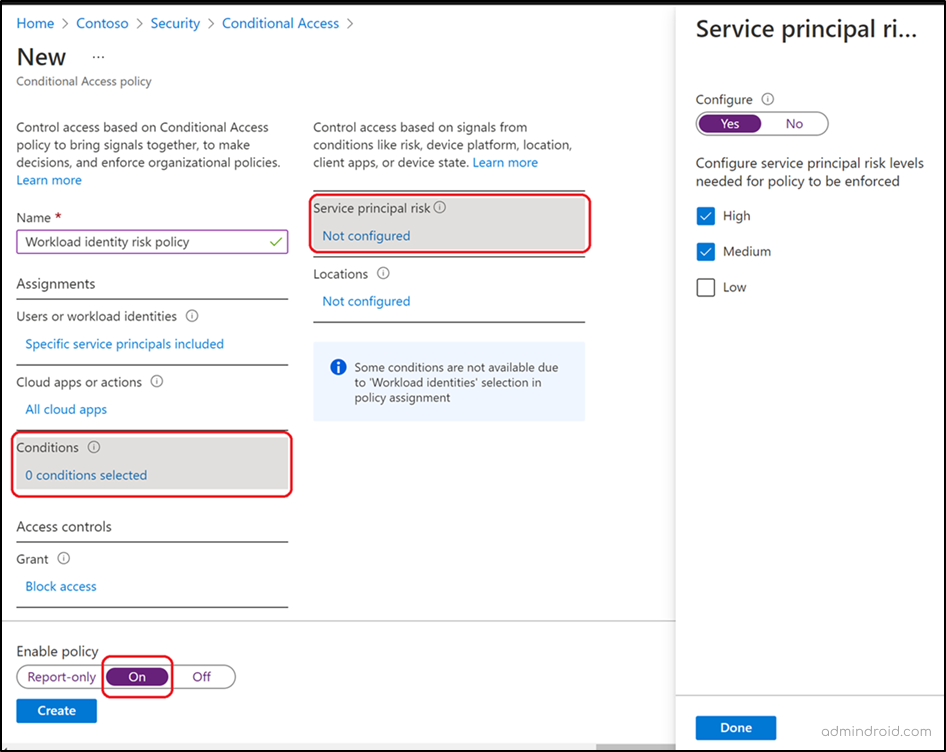
To set up a Conditional Access policy to address user risk factors, such as leaked credentials, you can follow the steps outlined below.
- Navigate to Microsoft Entra admin center → Protection → Conditional Access.
- + Create new policy → Name → Give a suitable name.
- Assignments → Users → All users.
- Target Resources → Select All cloud apps or select specific apps
- Conditions → User risk> set Configure to Yes → Select the risk level (High/Medium/Low) → Done
- Access controls →Grant → Grant access → select Require authentication strength option and Require password change→ Select.
- Finally enable the policy to ‘On’ mode and continue to save the policy.
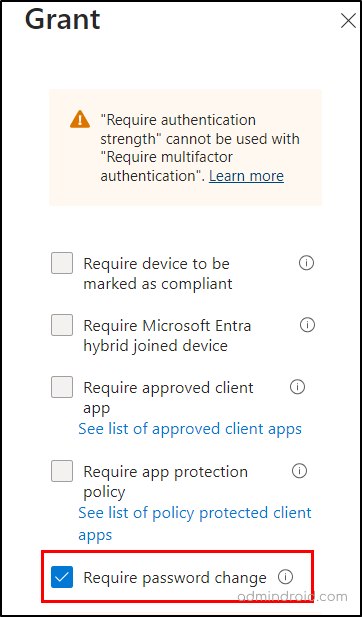
Once configured, the policy will mandate both multi-factor authentication and password resets for users identified by leaked credential detection feature. This proactive approach prevents attackers from using stolen credentials, while legitimate users can access resources with their new passwords. Furthermore, make sure to monitor Conditional Access policies regularly to check the policy enforcement in your organization.
You may have a question in mind: “Is the leaked credential detection limited to user account credential compromises?”. Let’s find the answer in the topic below.
Secure Workload Identities with Leaked Credential Detection
The answer to the above question is NO! Because the same as Microsoft 365 user account credentials, if application credentials are publicly posted, they will also be detected and displayed in the leaked credential detection. Yes, Microsoft has extended Entra ID protection for workload identities too! To check this out, we have explained to you with a scenario “Simulate leaked credentials in GitHub for workload identities”.
Note: These detections are visible only to Workload Identities Premium customers.
In this scenario, we aim to simulate a situation where an organization’s application credentials are leaked on GitHub public repository. To achieve this, follow the steps below.
- You need to register an application in Azure AD or else you can make use of the stale applications.
- Note down the respective app credentials such as client secret, application Id and all.
- Make sure to disable the application by navigating to Identity → Applications → Enterprise Application Properties → Enabled for users to sign-in → No.
- Create a public GitHub repo → Upload the app credentials → Commit by saving the file as .txt.
By following these steps, you have successfully simulated a scenario where application credentials were exposed in a public GitHub repository. Within 8 hours, the leaked credential detection in Microsoft Entra Identity Protection will provide details of this exposure.
To identify risky workload identities, follow the navigation below.
Microsoft Entra admin center → Protection → Identity Protection → Risk Detection → Workload identity detections.
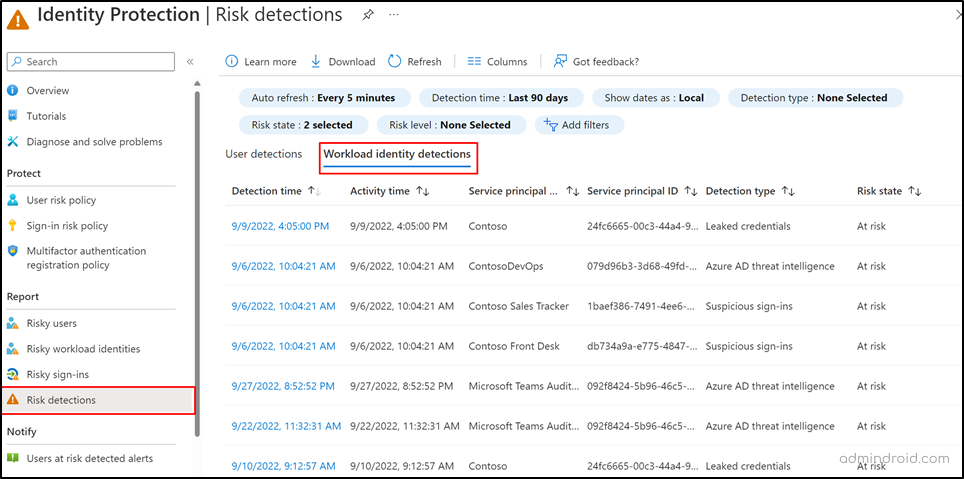
Remediate Risky Workload Identities with Conditional Access
In addition to detecting leaked credentials, you can further enhance the security using Conditional Access policies for workload identities.
- These policies enable you to implement password resets and multi-factor authentication based on the application risk score, offering a comprehensive approach to safeguarding your organization’s assets. For this too, you need a workload identities premium license.
- Also, admins can temporarily block access to applications, as a proactive measure to prevent unauthorized access.
Final Thoughts
Thus, in the battle to protect your Microsoft 365 environment, Microsoft’s free credential compromise identification is your secret weapon! With continuous vigilance of risk detection reports, you’re not just defending, you’re winning the cybersecurity game.
Let’s face it: the future is now. We are already living in a cyber society, so we need to stop ignoring it or pretending that is not affecting us.
Marco Ciapelli
I hope this blog seems informative for you to gain about the necessary leaked credential detection. Furthermore, feel free to reach us in the comment section for any assistance needed.