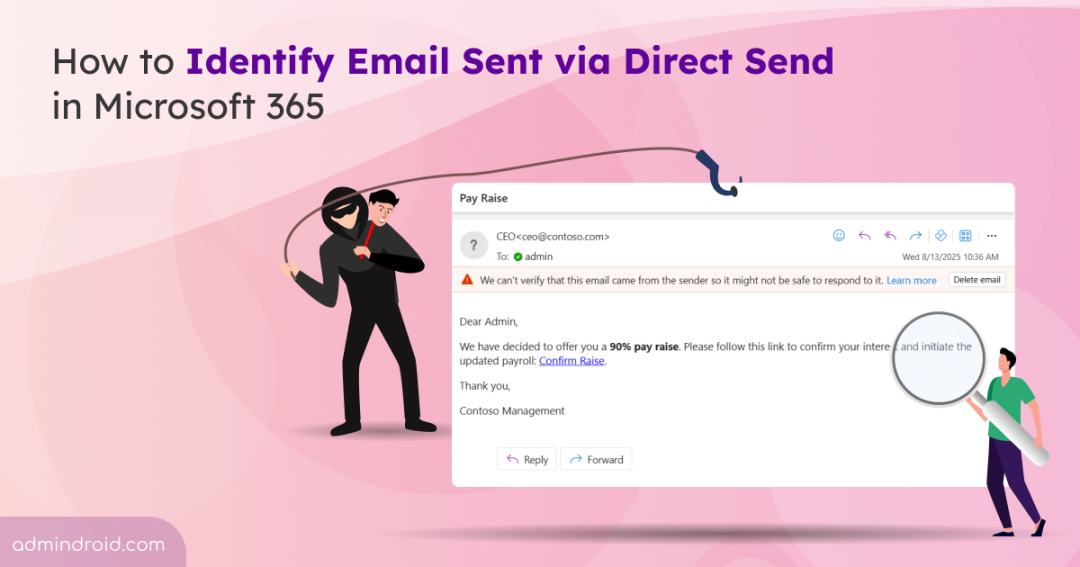
Direct Send in Microsoft 365 allows internal emails to be sent without authentication, which attackers can easily exploit to send phishing messages that appear to come from trusted accounts. This makes it critical for Microsoft 365 admins to monitor emails sent via Direct Send and distinguish legitimate emails from malicious ones.
What makes this even more challenging is that there is still no dedicated report to monitor Direct Send email activity. Without this visibility, it’s difficult to know whether your organization’s Direct Send functionality is being used correctly by internal users or abused by attackers.
To overcome this blind spot, our blog shows you how to identify Direct Send email activities in your Exchange Online environment. This will help you detect suspicious emails sent using the Direct Send feature before they turn into security incidents.
Why is Monitoring Direct Send Email Activities Important?
The simplicity and lack of security checks in Direct Send make it prime way for attackers to send fake voicemail alerts, invoices, payments requests, often attaching PDFs or QR codes that lead to phishing sites designed to steal users’ Microsoft 365 credentials. In addition, the mail relay endpoint follows predictable patterns, and common internal addresses such as ‘hr@contoso.com’ are easy to guess, making spoofing very simple. Therefore, monitoring Direct Send email activities helps detect misuse and allows early action to prevent breaches.
How to Detect Emails Sent Through Direct Send in Exchange Online?
Currently Microsoft is working on a dedicated report for Direct Send traffic, giving admins a clear overview of which messages would be affected if the feature is blocked. Meanwhile, you can use the following methods to get all emails received without an inbound connector and spot the ones sent via Direct Send.
- Review historical message trace report
- Leverage message trace in Exchange Online
- Use Microsoft Defender advanced hunting
Review Historical Message Trace Report to List All Directly Sent Emails
To find emails sent via Direct Send, you can run a historical message trace in Exchange Online to pull up email delivery logs from the last 90 days. To do that,
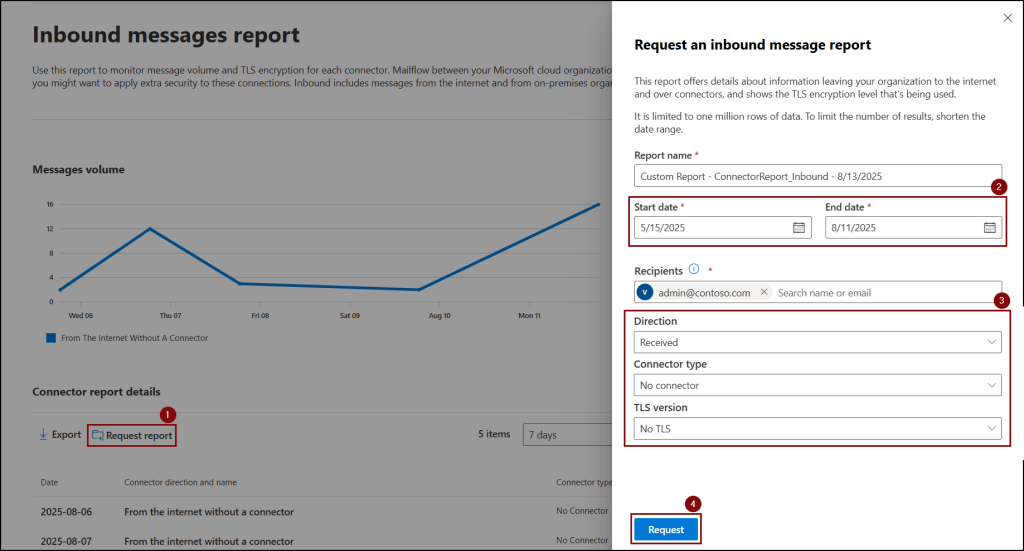
- Navigate to the Exchange admin center > Reports > Mail flow and select Inbound messages report from the list.
- Next, click on the Request report and modify the Start & End date based on your requirement.
- Click the Recipients dropdown and choose the desired recipients to receive the inbound message report.
- Then, ensure that Received and No connector are selected under Directions and Connector type appropriately.
- Finally, set TLS version to No TLS and hit Request to receive a report on all inbound emails received without a connector to identify Direct Send emails.
You can also use the following PowerShell cmdlet to perform the historical message trace on all inbound emails received without a connector.
|
1 |
Start-HistoricalSearch -ReportTitle DirectSendMessages -StartDate <MM/DD/YYYY> -EndDate <MM/DD/YYYY> -ReportType ConnectorReport -ConnectorType NoConnector -Direction Received -TLSUsed No Tls -NotifyAddress <YourEmailAddress> |
Replace the place holders <MM/DD/YYYY> and <YourEmailAddress> with appropriate values before executing the cmdlet.
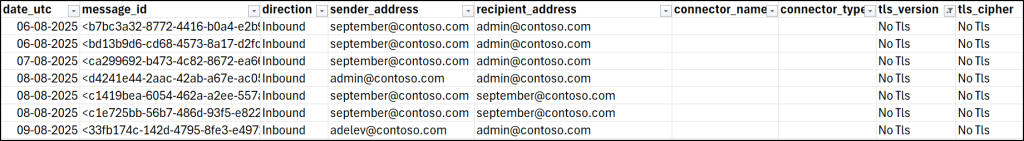
Find Emails Sent via Direct Send Using Exchange Online Message Trace
To identify emails sent using Direct Send, start by retrieving all internal messages sent to internal users using Exchange Online Message Trace V2. Then, review these emails for unexpected external IP addresses or subjects.
Run the message trace using the following PowerShell cmdlet by replacing the placeholders with your domain name, desired date range, and report export path.
|
1 |
Get-MessageTraceV2 -SenderAddress "*@<YourDomain>.com" -RecipientAddress "*@<YourDomain>.com" -StartDate <MM/DD/YYYY> -EndDate <MM/DD/YYYY> | Export-CSV <OutputCSVFilePath> -NoTypeInformation -Encoding UTF8 |
Next, verify the suspected emails using the following cmdlet.
|
1 |
Get-MessageTraceV2 -MessageId "<MessageID>" | Get-MessageTraceDetailV2 | Format-List |
In the results, look for the ConnectorName field. If the field shows your expected connector name, the message was delivered through that connector. If it’s blank or different from the expected connector, the email was sent via Direct Send.
Then, validate those emails’ SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records to confirm whether it is phishing emails or legitimate messages. The phishing emails sent via Direct Send will typically show SPF=Fail or SoftFail, DKIM=none, DMARC=fail, as these are strong indicators of spoofing or unauthenticated senders.
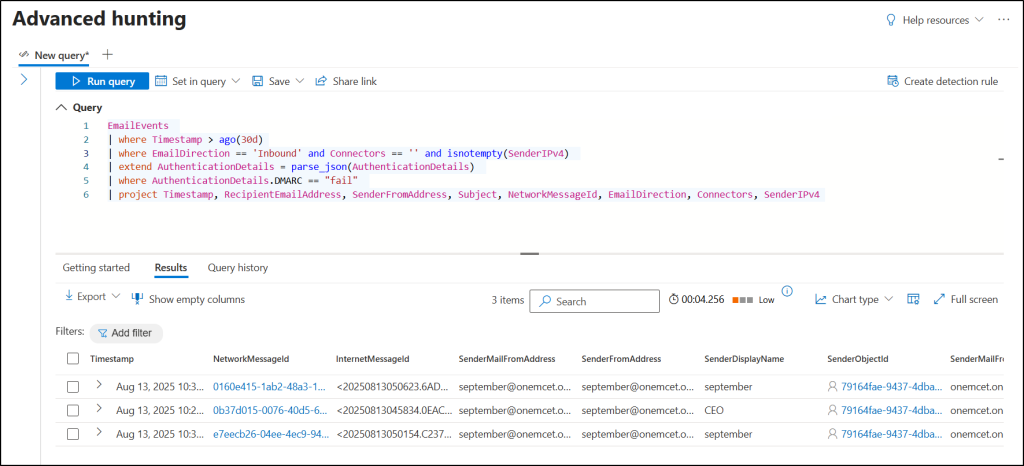
Leverage Advanced Hunting in Microsoft Defender to Review Direct Send Emails
You can use the advanced hunting feature in the Microsoft Defender portal to run Kusto Query Language (KQL) queries and get detailed insights into Direct Send emails across your organization.
- Login to the Microsoft Defender admin center.
- Navigate to Investigation & response > Hunting > Advanced hunting.
- Enter the following KQL query under the Query field.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
EmailEvents | where Timestamp > ago(30d) | where EmailDirection == 'Inbound' and Connectors == '' and isnotempty(SenderIPv4) | extend AuthenticationDetails = parse_json(AuthenticationDetails) | where AuthenticationDetails.DMARC == "fail" | project Timestamp, RecipientEmailAddress, SenderFromAddress, Subject, NetworkMessageId, EmailDirection, Connectors, SenderIPv4 |
- Finally, click Run query to find emails received without an inbound connector that fail the DMARC check, helping you quickly spot Direct Send messages in Microsoft 365.
Final Thoughts
While Microsoft 365 offers multiple ways to detect and investigate emails sent via Direct Send, monitoring alone is not enough to stop the threat. The safest approach is to proactively block Direct Send emails. Enabling Microsoft’s Reject Direct Send feature closes this loophole by blocking any anonymous messages sent from your own domain to your organization’s mailboxes that are not routed through an inbound connector. I hope this blog helped you identify email sent via Direct Send for better threat protection. If anything is unclear or you need help, feel free to ask in the comments.