On Day 11 of Cybersecurity awareness month, learn to secure your domain from being spoofed today. Stay tuned for more blogs in the Office 365 Cybersecurity blog series.
Nowadays, impersonation attacks like phishing, spoofing, etc., have become more common. As the usage of third-party tools has become massive, there are more chances of our identity being spoofed by attackers. So, we need to adopt email authentication methods to avoid such attacks. Though there are various methods, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC top the list. When considering Microsoft 365, we need to handle outbound emails in a way to retain our domains’ trust among email receivers. We don’t need to bother about inbound emails, it will be handled by Microsoft itself.
It takes 20 years to build a reputation and a few minutes of cyber-incident to ruin it
-Stephane Nappo
As the quote tells us, we need to retain our domain reputation against being phished or spoofed. So, we recommend implementing these email standards to ensure your domain isn’t used for spoofing.
Note: Before going further, be clear that these methods are used to ensure that our domain will not be spoofed by attackers.
What is SPF?
The Sending Policy Framework (SPF) will help the receiving servers to validate that the email sent from a mail server is authorized or trusted. The SPF record is a TXT record in your DNS which includes the list of IPs or domains of the authorized email senders.
How Does SPF Work?
- When you send an email, the receiving server will perform a DNS lookup and verify the SPF record in your DNS.
- If the received IP address or domain in the ‘Mail From’ field of your email header matches with your DNS record, the server will consider it as legitimate and accept the email. Else, it will reject or quarantine the email message.
SPF Configuration
- When you configure a domain for Exchange Online, Microsoft will automatically handle SPF for your domain.
- If you are using one or more custom domains or sub domains, you can configure SPF based on your organizational requirements.
Scenarios in Which the SPF Fails
- If you configure to auto-forward your specific incoming email to your personal email address or others, the SPF check may fail. Because, the header might be changed when forwarding.
- The DNS lookup limit for SPF is limited to 10 for each email. If the lookup limit exceeds for an email, the SPF check fails.
In these above scenarios, even a legitimate domain will fail in the SPF checks and create a false positive result. To avoid this, you can configure DKIM or DMARC along with SPF.
What is DKIM?
The Domain Key Identified Mail (DKIM) will digitally sign your email messages and the receiving server will decrypt and realize that the content is not tampered and the domain is authorized.
How Does DKIM Work?
- When you send an email, it will be digitally signed, and the body content and header are appended to the email as a hash value for verification.
- While receiving, the server will query your DNS for the public key and the respective domain as per the DKIM data of your email and validate the body content and header with the help of your DNS’s DKIM record.
- If it matches, the DKIM check will pass. Else, the check will fail.
DKIM Configuration
- Microsoft will provide DKIM for your custom domains or sub domains by default. However, having your own dedicated DKIM record for each domain is recommended for better recognition among the email services.
- Explore how to configure DKIM in your Office 365 environment via Admin Center or PowerShell.
Scenarios in Which DKIM Fails
- If you are using third-party tools to send email, they must ensure that the DKIM is configured using their own DNS for better trust. Else, the DKIM check fails in the receiving server.
- After publishing the DKIM records, you need to enable the DKIM to work properly.
- Some Mail Transfer Agents may modify the message body while transferring the email content. In such situations, the DKIM check fails.
Let’s see about DMARC and how it will help to secure your domain from impersonation attacks.
What is DMARC?
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) uses SPF and DKIM results and verifies two metrics such as SPF alignment and DKIM alignment. Even if the SPF and DKIM check passed successfully, there may be chances that the DMARC check fails. Because, DMARC will focus on verifying the ‘From’ address of the email against the SPF and DKIM check.
DMARC will give you the ability to know whether your domain is being used by someone to spoof. Thus, enabling better security.
What is SPF Alignment and DKIM Alignment?
The DMARC will check the below two alignments.
SPF Alignment
In SPF check, the IP address or domain in the ‘Mail From’ property of the email header will only be checked in your DNS. Whereas DMARC will verify whether the domain in ‘Mail From’ matches the domain or sub-domain of the sender. Thus, DMARC checks whether the ‘From’ address will match the ‘Mail From’ address.
DKIM Alignment
DKIM validates the configured domain in the email’s DKIM data and the respective DNS record. But, DMARC checks whether the domain mentioned in the ‘From’ field will match the ‘d=domain’ tag.
How Does DMARC Check Work?
- The email receiving server first collects the pass/fail results of SPF and DKIM.
- If at least one of these methods passes, then the server will go for DMARC check i.e, SPF alignment and DKIM alignment check.
- If any one of the alignment checks passes, the DMARC check will pass and the message gets delivered to the receiver. Else, it will be rejected or quarantined as per the DMARC configuration.
Note: When configuring DMARC, it is recommended to have both SPF and DKIM as well. Not configuring will lead to failure of those tests impacting DMARC success rate.
DMARC Configuration
- Explore how to configure DMARC for your domain in Microsoft 365.
- When implementing DMARC, it is recommended to implement it for half of your emails first and analyze the impact. Then slowly increase the percentage till implement it for all of your emails.
- DMARC provides aggregate reports to analyze your domains’ DMARC check failures periodically. You can get it to your configured email.
What are the Impacts of Third-Party Email Providers you Use on These Authentication Configurations?
- Most third-party email providers will handle SPF by themselves. If not done, you may have to reach the service providers to configure it.
- Alike SPF, you must reach the respective service providers for DKIM as well. Providers like Amazon SES, MailChimp, etc., will have their own documents to configure DKIM seamlessly.
- Unlike SPF & DKIM, DMARC needs additional configurations to be performed as it verifies the alignment! For SPF, you have to modify the Mail From domain of your service provider. When it comes to DKIM, each provider would handle it differently; you may have to create the DKIM keys through the providers or you have to do it manually as per their documentation.
To Summarize…
Thus, I have covered SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and its working, to give you a clear picture of these authentication methods. Also, we have seen how to get better recognition when using third-party service providers. Before concluding, I have a few tips for you on handling the failures of these features.
How to Handle SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Check Failures?
- If the SPF record fails when you configured auto-forwarding, you can use ‘redirect’ feature in this case. Because, when forwarding the header may get changed. But while redirecting, the header remains the same.
- If you want to configure DKIM, and you are using any third-party tools which modify the content like content formatting or whitespaces, the DKIM check will fail. In this case, you can use ‘C’ tag and decide whether strictly no modification will be accepted or simple modification in headers and body will be accepted. Thus, you can avoid such false positive failures.
- When using DMARC, If SPF check fails, the DMARC for SPF alignment will also fail. Similarly, if DKIM check fails, the DMARC for DKIM will also fail. So, ensure to check SPF and DKIM failure first, when investigating DMARC issues.
- You can analyze the DMARC check failure issues using the DMARC reports to avoid issues in the future.
- If you face DMARC errors in email sent via third-party providers, you can configure alignment mode ‘Relaxed’ for both SPF and DKIM separately. Most third-party providers require this to be relaxed.
Still Thinking What to Configure for Your Domain?
Be clear about the three email authentication methods and their usage. As per Microsoft, only 9% of domains of companies in the Fortune 500 publish strong email authentication policies as of march 2018. Others may get a high chance of spoofing. So, try to configure as much as possible so that it works smoothly for your management. The more the better!
Adopting these email authentication methods verify legitimate domains, which are done in servers. In addition, many threat policies help to prevent phishing, spoofing, malicious links, etc., which should be adopted and configured internally in the organization. The above-mentioned methods require a keen eye to configure, and they may affect mail flow if configured wrongly. So, many organizations will rely on threat policies alone to prevent such threats.
AdminDroid – Savior for Admins in Email Monitoring
For monitoring the configured threat policies and changes made to them, AdminDroid provides you with all-inclusive details to detect unnecessary modifications. Also, the email dashboard gives you an overview of Microsoft 365 mail traffic stats, including spam, malware, phishing, and spoof stats with its top recipients.
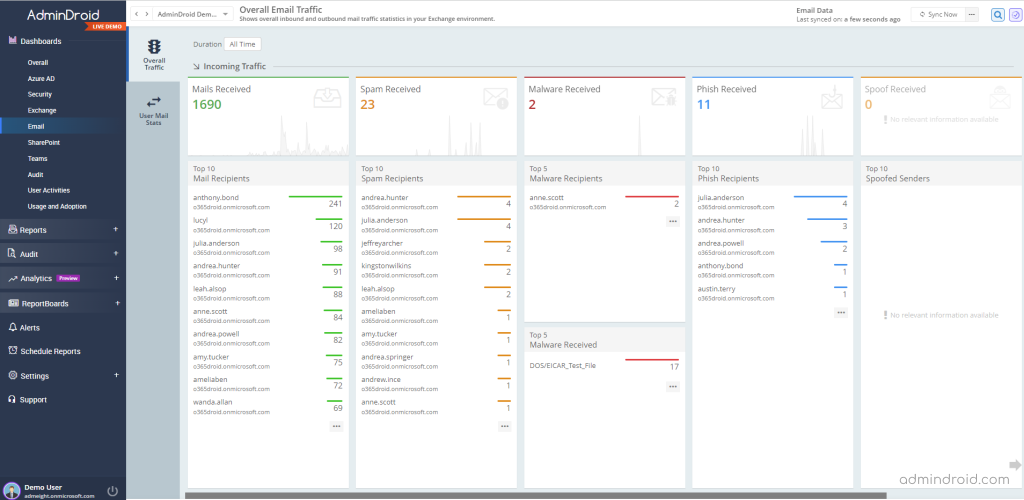
From AdminDroid, you can also gain details on Exchange Online mail protection reports mentioned below.
Phish Mails & Detections
- Incoming & outgoing external phish mails
- Internal phish mails
- Daily phish mails sent / received by users
- Top phish senders & receivers
- Overall threat protection stats by phish detections
- Spoof based phish detections
- Filter based phish detections
- Impersonation phish detections
- Reputation phish detections
- Detonation phish detections
- File based phish detections
- URL based phish detections
- Campaign & other phish detections
- Anti-phish policy configuration changes
- Phishing filter configuration changes
Spoof Mails & Detections
- External & Internal spoof mails
- Top spoofs
- Overall threat protection stats by spoof detections
Likewise, you will get details for spam and malware emails too. Along with that, gain details on peak hours, slack hours, inactive mailboxes, active hours, and more based on email analysis in your organization.
Want to Know How AdminDroid Enhances Your Email Monitoring Experience?
- Visualize every nook and corner of your organization’s email activity with cutting-edge stats and deeper analysis.
- Get instant alerts on suspicious emails, unusual mail flow, malicious mail detections, and more.
- Schedule your reports to monitor prominent data anywhere at any time.
- Delegate your email administrator and allow access only to the email dashboard and email-related reports ensuring the least privileged access.
No more wait! Start exploring the AdminDroid email monitoring tool today and improve your organization’s security a step further.
Don’t be bound by email protection reports! Indulge in 1800+ reports with in-depth details, 30+ analytical dashboards with appealing insights, and numerous features of AdminDroid to effectively manage every Microsoft 365 service right from Azure AD, Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, Microsoft Teams, Power BI, and more.
I hope this blog will help you to understand email authentication methods better to prevent impersonation attacks in your organization. For safeguarding our organization internally, we also have various security measures like External tagging, blocking auto-forwarding, etc. But, to ensure that our domain is not used for such attacks, we should adopt these authentication methods. Share your thoughts and suggestions through the comment sections and social media pages.