A recent post from Microsoft has left admins uncertain and with a lot of queries flashing in their minds. Microsoft said that the Azure teams will begin the gradual rolling out of additional tenant-level security measures this July that require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all Azure users. Unfortunately, no additional details about the enforcement of MFA and its impacts were conveyed officially. We all know that Microsoft’s Secure Future Initiative focuses on enhancing security among organizations. Implementing new identity protections and MFA at the tenant level is one of the parts of engineering advancements to improve security at its best.
Impacts of Enforcing MFA for All Azure Users
When Microsoft announced its plan to enforce MFA for all Azure users, it sparked a flurry of questions and concerns across social platforms. Here are some answers to the queries customers are concerned about!
- Will service accounts be impacted by this change? How many tokens do they need from Microsoft for access?
- Usually, break glass accounts were excluded from MFA for emergency purposes. Will this roll-out include these accounts?
- What about guest users in Entra ID?
- How will Microsoft enforce this at the tenant-level? Security defaults or Conditional Access? Security Defaults doesn’t allow exclusions in MFA and if this change is added, it will make things complicated and break stuff in many cases.
- What method should users use for authentication? What for users who may not have smartphones for using the authenticator app?
- Is this roll out applicable only for users accessing Azure portals or all M365 users?
- Mobile phones are banned inside the classroom. How will it impact educational tenants? This might force schools to move to Google!
- Few are saying that they are unable to use Microsoft Entra’s MFA solution as the Conditional Access is locked behind the Entra ID Premium license.
- IT admins felt that it would create a burden, especially when implementing in large organizations.
Updated on 17/05/2024
In response to widespread concerns from admins and customers about enforcing MFA at the tenant level, Microsoft came up with much-needed answers.
What is the scope of this rollout?
All users signing into the Azure portal, CLI, PowerShell, or Terraform to administer Azure resources will be required to use MFA.
Will there be exceptions for service accounts and break glass accounts?
Service principals, managed identities, workload identities, and similar token-based accounts used for automation are excluded. Microsoft is still collecting customer feedback for scenarios like break glass accounts and special recovery processes. Also, MS recommends updating the break glass accounts to use FIDO2 or certificate-based authentication as both methods will satisfy the MFA requirements.
Update (07/08/2024): Break glass accounts will also be included in the MFA enforcement
As part of the MFA enforcement rollout, emergency accounts (break glass accounts) will also needs to be registered with MFA. Microsoft strongly suggest to configure different authentication method for at least one of the emergency accounts in the organization. As previously said, admins are recommended to update emergency accounts to use FIDO2 or certificate-based authentication methods.
Will students, guest users, and other end users be affected by the new enforcement policy?
Students, guest users, and other end users will only be affected if they are signing into Azure to manage Azure resources. This policy does not apply to apps, websites, or services hosted on Azure.
What are the supported MFA methods for authentication?
All supported MFA methods, such as Microsoft Authenticator, FIDO2 security keys, SMS, voice calls, etc., can be used. Also, external MFA solutions can be used to meet MFA requirement which is currently in public preview with external authentication methods.
How the MFA enforcement will be implemented?
The MFA requirement will be implemented by Azure, and Microsoft Entra Sign-in logs will show it as a source. This will be implemented on top of any access policies configured in the tenant.
For instance, If security defaults is enabled or your tenant is using Conditional Access policies in MS Entra, your users will not see any change as the MFA is already required for Azure management. Likewise, if your tenant has any existing strong CA policies configured that require MFA for Azure, such as phishing-resistant MFA, those policies will continue to be enforced, and the users will not see any changes.
Will there be any exceptions for tenant-level MFA enforcement?
There will be no opt-out option, but an exception process will be available for cases with no alternative solution. Details about the exception process will be communicated through official notifications.
Despite these assurances, concerns about the enforcement method and the specifics of break glass accounts still linger. But fear not! The Azure team promises to keep you in the loop with additional details and rollout dates. So, let’s stay hopeful that Microsoft will address these concerns and empower customers with the control they need.
Update (16/08/2024): Phased Rollout Timeline for MFA Enforcement
Microsoft comes up with a rollout timeline update for MFA enforcement requirements for Azure portal sign-ins.
Phase 1: The first phase of this rollout will begin October 15, 2024, requiring mandatory MFA to access the Microsoft Entra admin center, Azure portal, and Intune admin center.
Phase 2: Starting in early 2025, MFA enforcement for Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, Azure mobile app, and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools will gradually roll out to all tenants.
Update on 11/11/2024: Microsoft 365 admin center is also included (starting February 3rd, 2025) in the Phase 2 rollout.
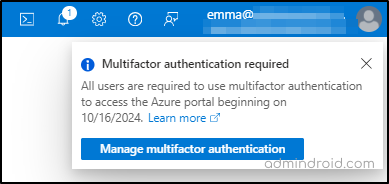
Note: For both phased rollouts, MS will notify global admins about the expected enforcement date for their tenant 60 days prior by email and Azure Service Notifications. The countdown for the enforcement begins only when the global admins receive their first notification from Microsoft as shown below.
In addition, they will send periodic reminders to global admins between the first notification and the beginning of enforcement for their tenants.
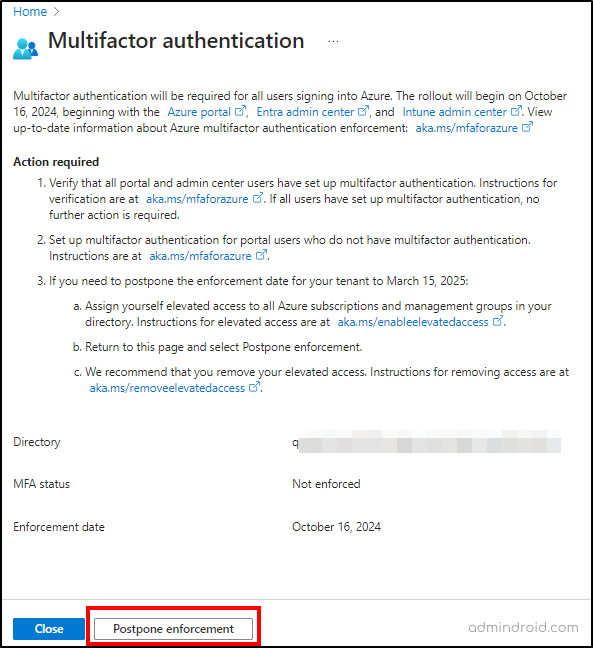
MFA Enforcement Portal
If you select ‘Manage multifactor authentication’ in the notification, you will be navigated to the dedicated MFA portal. In the portal, you will find additional details, such as enforcement status, enforcement date, actions required, etc. You can also able to postpone the MFA enforcement by clicking on the ‘Postpone enforcement’ option, if required.
Identify Azure Users Impacted for MFA Enforcement in Your Tenant
By utilizing the below methods, you can detect who is signing into Azure with and without MFA in your tenant. So, you can also decide to enforce MFA now, before the MFA enforcement from Microsoft.
- Export a list of users and their authentication methods using the Export-MsIdAzureMfaReport PowerShell command.
- You can use the Multifactor Authentication Gaps workbook in Entra ID.
- You can use the below App IDs in your queries:
- Azure portal: c44b4083-3bb0-49c1-b47d-974e53cbdf3c
- Azure CLI: 04b07795-8ddb-461a-bbee-02f9e1bf7b46
- Auzre PowerShell: 1950a258-227b-4e31-a9cf-717495945fc2
What is the Reason Behind the Enforcement of MFA for All Azure Users?
As the remote work culture is growing everywhere, users are accessing resources outside the office environment using various devices and networks. This remote culture has increased the potential for unauthorized access and demands the usage of MFA among organizations for enhanced Microsoft 365 security.
Previously, using ‘security defaults’ MFA could be enabled for all users in the organization. Still, most of the user accounts are not enabled with MFA, and most organizations do not enforce it. As a result, Microsoft found that 99.9% of compromised accounts did not use MFA. As they are moving towards having a secure future, they have planned to implement MFA at the tenant level.
Crucial Role of MFA for Microsoft 365 Security
MFA is a key feature in identity and access management, which ensures that only authorized users can access Microsoft 365 services and resources. It prevents unauthorized access to user accounts effectively, thereby reducing the attack surface in the organization. A report from Microsoft found that 99.99% of accounts with MFA remain protected. And the best part with MFA:
- Reduces the overall risk compromise by 99.22%
- Reduces 98.56% of account compromises happened due to leaked credentials.
- Helps to comply with compliance security standards and regulations, such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, and NIST
- Helps to prevent password attacks, brute force attacks, unauthorized logins, etc.
There are various types of MFA authentication methods like SMS, Microsoft authenticator app, etc. Though both are used for additional verification, the authenticator app is considered more secure than SMS. Also, admins can implement strong MFA methods like phishing-resistant MFA, system-preferred MFA, and more. Due to the growing culture and the increasing cyberattacks, organizations recognize that configuring MFA is a must-needed step for security.
However, admins need to be aware of MFA fatigue attacks and how to overcome it for better security. Tell us what concerns you have regarding this feature through the comments section.