SharePoint Online admin center allows admins to manage their SharePoint sites and users. To secure their organization data from intruders, Microsoft provides various settings and policies to manage content sharing and access in SharePoint Online. Configuring effective and required policies helps to establish reliable control over sensitive information shared with external users. Also, it is recommended to set up a few basic configurations at the organization level to improve your security posture and avoid unwanted external data sharing. Also, they can be configured at site levels and applied to individual users or groups to control content sharing and access permissions on a specific site.
Now, let’s dive into the org-wide configurations to manage external sharing and access controls in SharePoint Online effectively.
SharePoint Online Sharing and Access Configurations
- Sharing policies in the SharePoint Online admin center
1. Configure Organization-level External Sharing Settings
2. Additional External Sharing Settings
3. Default Sharing Link for File and Folder in SharePoint Online - Access control settings in the SharePoint Online admin center
4. Unmanaged Devices Access Control Configuration
5. Enable Idle Session Sign-out in SharePoint Online
6. Control Access Based on Network Location
7. Block Apps That Don’t Use Modern Authentication
8. Audit SharePoint Online Sharing Activities
Sharing Policies in SharePoint Online Admin Center
Sharing policies control how users can share content within SharePoint sites to safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access. These policies can be used to,
- Set restrictions on external sharing.
- Control which external users are allowed to access your content.
- Manage how much control users should have over the shared content.
To control external sharing at the organization level, navigate to SharePoint admin center -> Policies -> Sharing.
1. Configure Organization-level External Sharing Settings
In the External Sharing section, you’ll see a slider for configuring how external users can access your SharePoint content. To limit external sharing in your SharePoint Online environment, you can configure the following options in SharePoint Online.
- Anyone: This setting allows anonymous users with a link to access the content without any authentication requirements.
- New and existing guests: This setting requires users to sign in using a Microsoft account or work or school account to access the content.
- Existing guests: This setting allows sharing to users who are already in your organization’s directory through sharing invitation or manual adding to access the content.
- Only people in your organization: External sharing will be turned off and users can’t share data outside your organization.
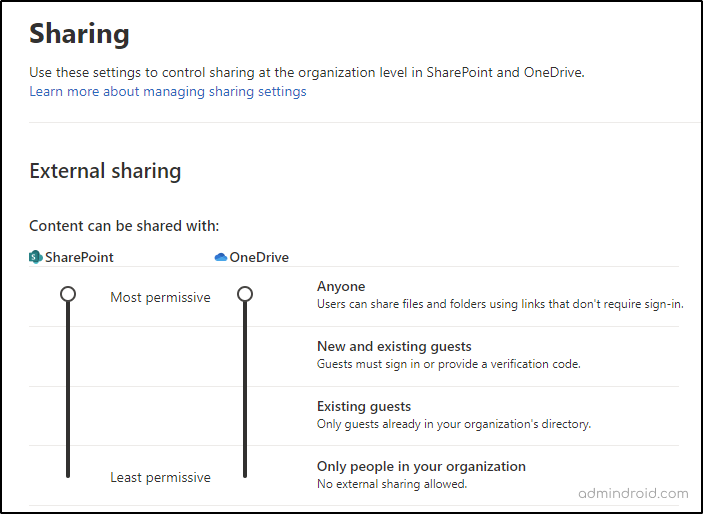
It’s important to note that the OneDrive setting cannot be less restrictive than the SharePoint setting. It means that if you configured SharePoint content to be available to new and existing guests, you can’t be able to set OneDrive to Anyone (anonymous) sharing. It must be the same or less permissive than SharePoint. The default settings for both SharePoint and OneDrive are set to Anyone.
2. Additional External Sharing Settings
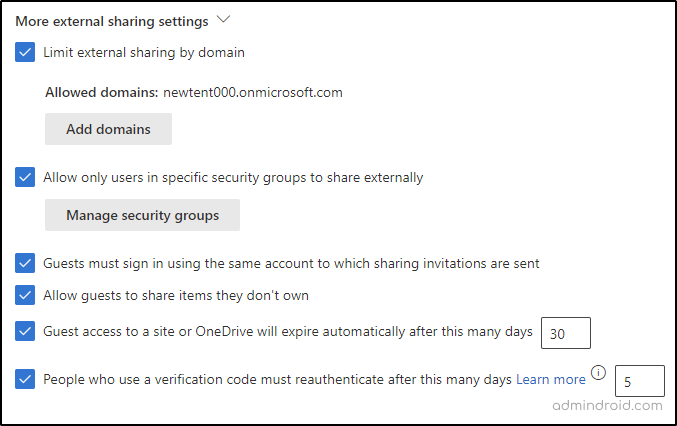
Limit external sharing by domain: If you want to limit the file and folder sharing to a specific domain, you can allow access to that domain alone. Alternatively, you can block a specific domain and allow all others to access your data. This setting can be configured for the entire organization or specific sites, depending on your requirements. This can help you control access to sensitive information and minimize the risk of data leaks.
Allow only users in specific security groups to share externally: If you want to limit external file sharing to specific users in your organization, you can create a Microsoft 365 security group and add those users to it. This group will only have permission to share content externally in SharePoint Online. However, it’s important to note that this setting cannot be configured at the site level.
Guests must sign in using the same account to which sharing invitations are sent: If you want your external users to sign in with the same account, they received the sharing invitation on, you can enable this option. If disabled, invited users can access the invitation by signing in using any account they prefer.
Allow guests to share items they don’t own: By default, guests can share files, even if they don’t have full access permissions. To restrict guest sharing of data they don’t own, you can uncheck this checkbox. This can help reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your organization’s data.
Guest access to a site or OneDrive will expire automatically after this many days: If you don’t want your externally shared content to be accessed indefinitely, you can set an expiration policy for the link to limit access. Thus, external users can’t access your files once the link has expired.
People who use a verification code must reauthenticate after this many days: To enhance security, you can set the number of days after which users need to reauthenticate when accessing shared content for users who use verification codes with permission levels other than the least restrictive level. For content shared with “Anyone with the link”, verification code is required.
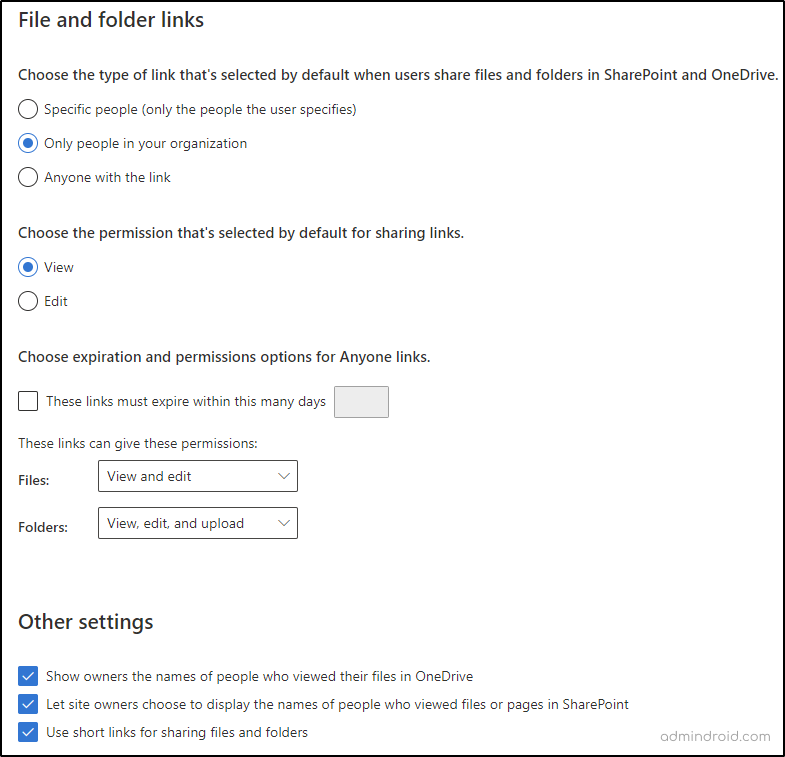
3. Default Sharing Link for File and Folder in SharePoint Online
In the file and folder links settings section of the SharePoint admin center, you can control the default sharing link type in SharePoint Online that appears when a file or folder is shared or copied. The default is “Only people in your organization,” but you can also choose “Anyone with the link” or “Specific people.” However, I recommend leaving the default as is to avoid anonymous links and prevent unwanted data exposure.
To improve security in anonymous sharing, the SharePoint admin center allows you to customize link expiration and link permissions for shared files and folders. You can set links to expire after a specific number of days and restrict “Anyone” links to only provide view permission.
In addition to these settings, there are other sharing settings available, such as controlling whether file owners can see who has viewed their files in OneDrive and whether site owners can allow users to see who has viewed a file, or page, or use short links for sharing files and folders.
Access Control Settings in the SharePoint Admin Center
Access control settings are used to restrict how users are allowed to access content in SharePoint Online and OneDrive. For restricting access, navigate to SharePoint admin center -> Policies -> Access control.
4. Unmanaged Devices Access Control Configuration
Device access policies in SharePoint Online control how users can access organization data from their devices. These policies can be used to enforce security requirements, such as requiring device encryption and limiting access to specific types of devices. Device access policies can help organizations maintain control over their SharePoint content and prevent unmanaged devices from accessing SharePoint and OneDrive.
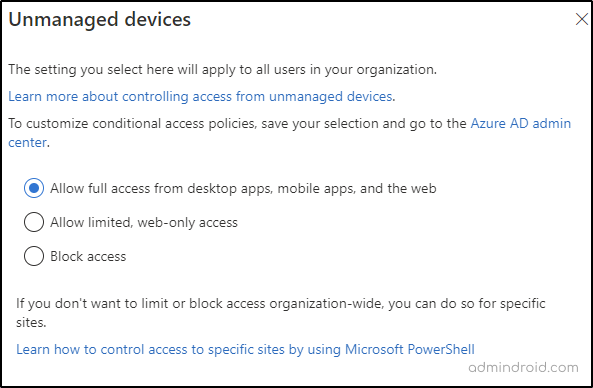
Allow full access from desktop apps, mobile apps, and the web: When this setting is enabled, users can access content from an unmanaged device. This setting is not recommended for organizations that require strict control over sensitive corporate data and information.
Allow limited web-only access: This setting allows users to access SharePoint Online content using a web browser on a device that isn’t enrolled in Intune or another MDM solution. This can be useful for users who need temporary access to content from a public or shared device.
Block file downloads in SharePoint Online: This setting prevents users from downloading files from SharePoint Online to an unmanaged device. Users can still view the files in the browser, but they won’t be able to download or sync them to the device.
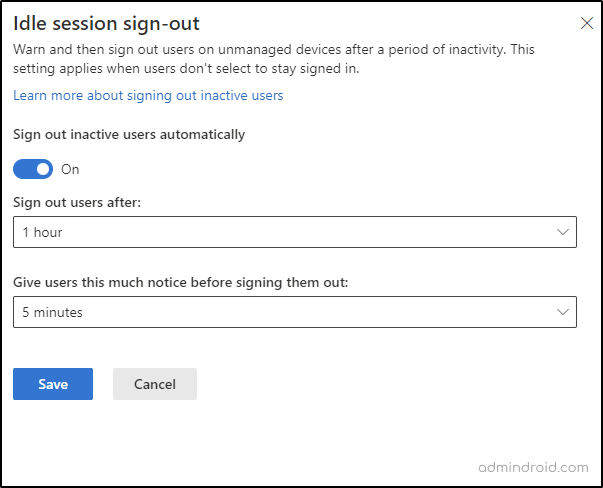
5. Enable Idle Session Sign-out in SharePoint Online
This setting controls how long a user can remain signed into SharePoint Online using an unmanaged device. It can help prevent unauthorized access to content if the user leaves the device unattended. By default, the setting is disabled.
When you enable idle session timeout setting, you can set the timeout value in minutes, ranging from 1 to 1440 minutes (24 hours), and you can set the time to notify users before signing out their session.
After the specified time elapses, the user’s session has been terminated, and they are prompted to sign in again to continue working with SharePoint Online content. It’s important to note that the Idle session timeout setting does not affect active sessions or tasks, such as uploading or downloading files. It only applies to idle sessions where the user is not actively engaged with SharePoint Online.
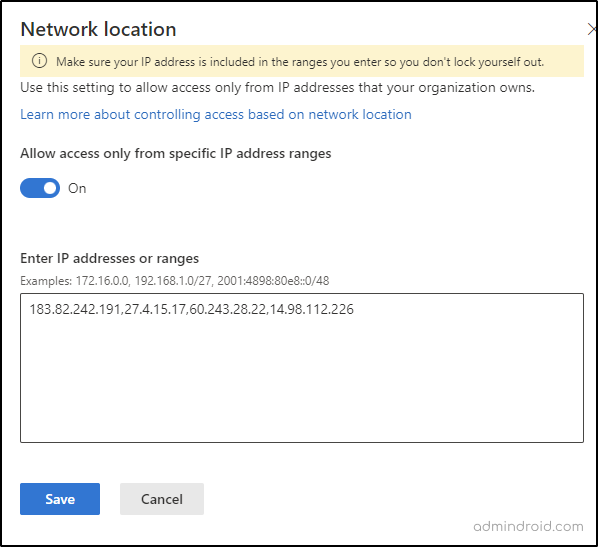
6. Control Access Based on Network Location
By default, SharePoint Online allows access from any location. However, you can restrict network location-based access to SharePoint by specifying the location of the users or groups based on IP address ranges. You can also specify whether to allow or deny access from those network locations.
Note: It can take up to 15 minutes for these settings to take effect.
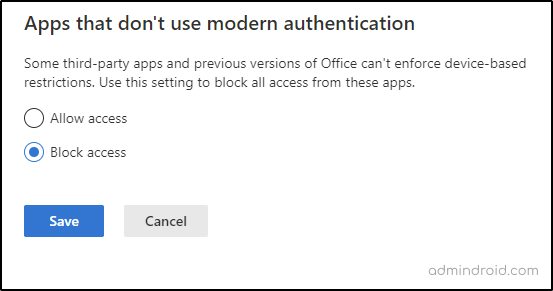
7. Block Apps That Don’t Use Modern Authentication
The “Apps that don’t use modern authentication” setting control apps that do not support modern authentication access to SharePoint Online. Overall, it is recommended to use modern authentication whenever possible and disable it if unnecessary.
By having all these features and policies in place, administrators can effectively manage sharing and access in SharePoint Online. Further, to keep track of the unwanted modifications made to the crucial configurations mentioned, admins can rely on the Microsoft 365 audit logs.
8. Audit SharePoint Online Configuration Changes
Monitoring configuration changes using audit logs helps to manage and secure the SharePoint Online data by detecting unnecessary changes and preventing data breaches.
The audit events logged for configuration changes in SharePoint Online include the following.
- Sharing policy changed: Any change to the settings in the sharing policy will be logged, such as default link configurations, external sharing settings, idle session time out settings, etc.
- Network access policy changed: Any change made to the network location setting based on IP ranges will be logged.
- Device access policy changed: Any change to the unmanaged device access control setting will be logged.
I hope this blog will guide you with the necessary configurations for managing sharing and access in SharePoint Online based on your organization’s requirements. Some of the above settings are also recommended in Microsoft’s Secure Score for SharePoint and can help boost both your Secure Score and organizational security posture. Feel free to reach us in the comments for any assistance.